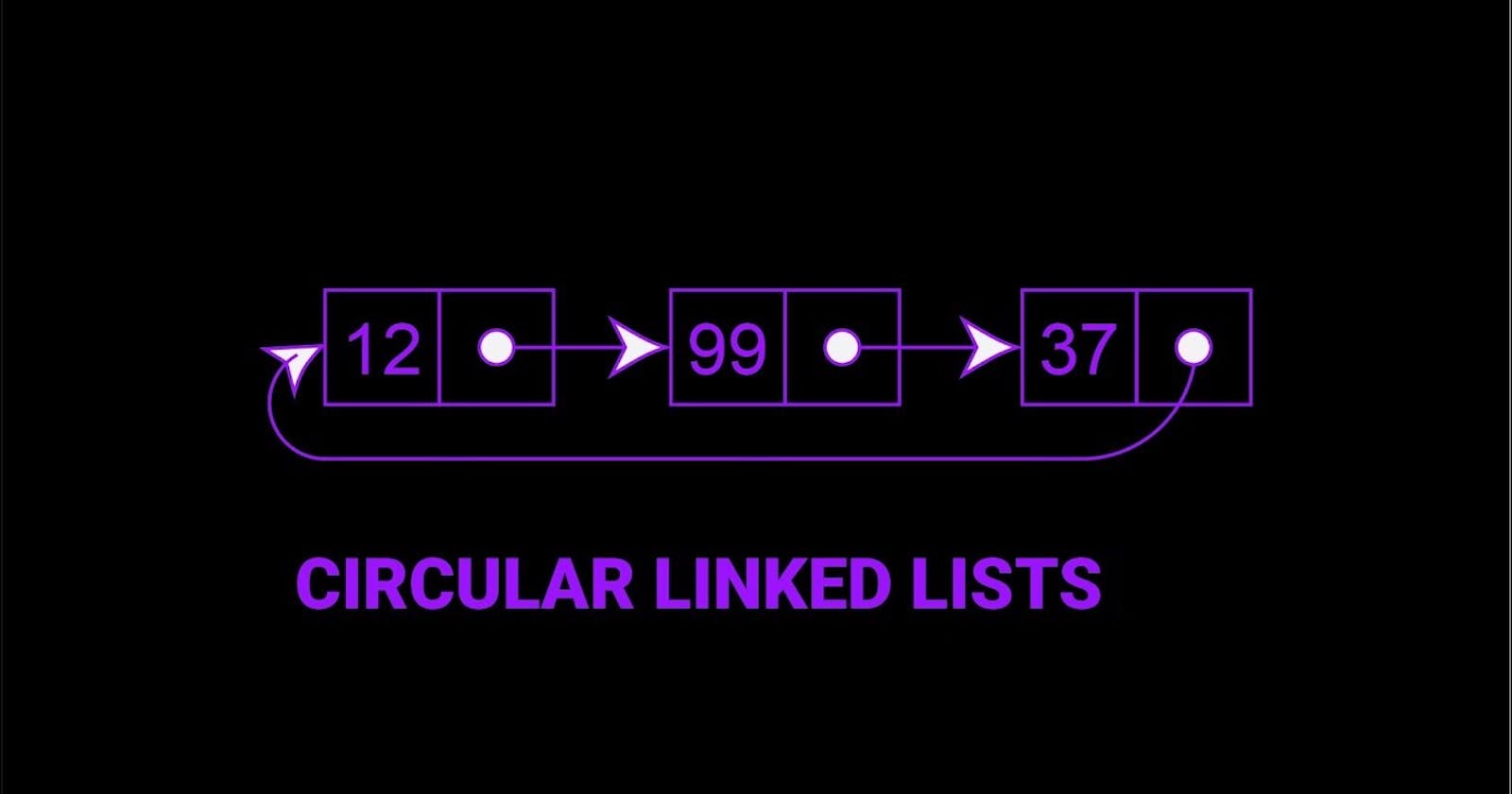
What is Circular Linked List 🎗️
A circular linked list is a type of data structure in which the last node points to the first node, forming a circular chain. In a circular linked list, there is no NULL at the end of the list. Instead, the last node points to the first node, forming a continuous loop.
Advantages of Circular Linked List 🎗️
Continuous loop: As mentioned earlier, a circular linked list forms a continuous loop, which means that there is no need to check for the end of the list. This can be useful in certain algorithms where we need to traverse the entire list.
Dynamic size: Like a regular linked list, a circular linked list can grow or shrink dynamically, depending on the needs of the program. This makes it a good choice for situations where the size of the list may change frequently.
Efficient traversal: Traversing a circular linked list is efficient because there is no need to check for the end of the list. This can be useful in certain algorithms where we need to traverse the entire list multiple times.
Disadvantages of Circular Linked List 🎗️
Inserting or deleting a node in a circular linked list can be more complex than in a linear linked list because the nodes are connected circularly.
Traversing a circular linked list can be more complex than a linear linked list because it is not possible to determine the end of the list. This means that a programmer must keep track of the starting node and the current node when traversing the list, and must also check for the condition where the current node has returned to the starting node, indicating that the entire list has been traversed.
A circular linked list is not suitable for implementing a stack or a queue data structure, because the nodes are not ordered linearly.
It can be more difficult to debug a circular linked list than a linear linked list because the nodes are connected circularly and it is not always clear where the list begins or ends.
A circular linked list is not suitable for implementing a data structure that needs to be sorted, because the nodes are not ordered linearly.
Overall, a circular linked list can be a useful data structure in certain situations, but it is not always the most efficient or practical choice, depending on the specific requirements of the application.
Types of Circular Linked List 🎗️
There are two types of circular linked lists:
Single circular linked lists
Double circular linked lists
In a singly circular linked list, each node contains a single link to the next node in the list. In a double circular linked list, each node contains two links: one link to the next node in the list and one link to the previous node in the list.
✅ Read more about: Singly Linked List
Coding a Circular Linked List in JavaScript 🎗️
Now let's take a look at the structure of a circular linked list. In a circular linked list, each node has two fields: a data field to store the data and a next field to store a reference to the next node in the list. The last node in the list points to the first node, forming a continuous loop.
function Node(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
To create a circular linked list, we need to have a head node and a tail node. The head node is the first node in the list and the tail node is the last node in the list.
function CircularLinkedList() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
Now let's implement some basic operations for a circular linked list:
Insertion
To insert a new node into a circular linked list, we can use the following steps:
If the list is empty, set the new
nodeas theheadandtailof the list.If the list is not empty, insert the new node after the
tailof the list.Set the new node as the
tailof the list.Set the next field of the new
nodeto theheadof the list, forming a circular chain.
Here is the implementation of the insertion operation in JavaScript:
CircularLinkedList.prototype.insert = function(data) {
let newNode = new Node(data);
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}
this.tail.next = this.head;
};
Deletion
To delete a node from a circular linked list, we can use the following steps:
If the list is empty, return null.
If the list has only one node, set the
headandtailto null.If the list has more than one
node, find the node to be deleted and update the next field of the precedingnodeto point to the nextnodeafter thenodeto be deleted.
Here is the implementation of the deletion operation in JavaScript:
CircularLinkedList.prototype.delete = function(node) {
if (this.head === null) return null;
let current = this.head;
let previous = null;
while (current !== node && current.next !== this.head) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
if (current === this.head) {
this.head = this.head.next;
this.tail.next = this.head;
} else if (current === this.tail) {
this.tail = previous;
this.tail.next = this.head;
} else {
previous.next = current.next;
}
};
Search
To search for a node in a circular linked list, we can use the following steps:
If the list is empty, return null.
If the list is not empty, start at the
headof the list and traverse the list until we find the desirednodeor reach the end of the list.
Here is the implementation of the search operation in JavaScript:
CircularLinkedList.prototype.search = function(data) {
if (this.head === null) return null;
let current = this.head;
while (current.data !== data && current.next !== this.head) {
current = current.next;
}
return current.data === data ? current : null;
};
Traversal
To traverse a circular linked list, we can use the following steps:
If the list is empty, return
null.If the list is not empty, start at the
headof the list and traverse the list until we reach the end of the list.
Here is the implementation of the traversal operation in JavaScript:
CircularLinkedList.prototype.traverse = function() {
if (this.head === null) return null;
let result = [];
let current = this.head;
while (current.next !== this.head) {
result.push(current.data);
current = current.next;
}
result.push(current.data);
return result;
};
Reverse
To reverse a circular linked list, we can use the following steps:
If the list is empty, return null.
If the list has only one
node, return the list.If the list has more than one
node, reverse the pointers of eachnodeto create a new list in reverse order.
Here is the implementation of the reverse operation in JavaScript:
CircularLinkedList.prototype.reverse = function() {
if(this.head === null) return null;
let current = this.head;
let previous = null;
let next = null;
while (current.next !== this.head) {
next = current.next;
current.next = previous;
previous = current;
current = next;
}
current.next = previous;
this.head = current;
};
Now let's put everything together and create a circular linked list:
let circularLinkedList = new CircularLinkedList();
circularLinkedList.insert(1);
circularLinkedList.insert(2);
circularLinkedList.insert(3);
console.log(circularLinkedList.traverse()); // [1, 2, 3]
let nodeToDelete = circularLinkedList.search(2);
circularLinkedList.delete(nodeToDelete);
console.log(circularLinkedList.traverse()); // [1, 3]
circularLinkedList.reverse();
console.log(circularLinkedList.traverse()); // [3, 1]
Conclusion 🎗️
In this blog, we have covered the fundamentals of Linked List. Its advantages and disadvantages. We learned how to create a circular linked list where we performed different operations like insertion, deletion, search, traversal and reverse.
Wrap Up 🎗️
Thank you for reading. If you find this helpful, leave a like, share, and follow me at, Syed Rafsan Raiyan to read more articles.